Smart Homes, Smarter Investments: Analysing the Impact of Home Automation on Property Values in Dubai & Abu Dhabi
1. Executive Summary
Smart home technology is no longer a novelty in the UAE’s real estate sector — it’s fast becoming a defining standard, particularly in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. Driven by government-led smart city initiatives, rising environmental standards, and evolving buyer expectations, smart-enabled properties are increasingly commanding price premiums, stronger rental yields, and longer tenant retention across both emirates.
This report explores how integrated home automation — from energy-efficient climate control to AI-assisted security — is influencing property values in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. It examines the scale of adoption among leading developers, the pricing differentials between smart and traditional homes, and the growing appeal of connected living among investors and end-users alike.
In Dubai, government initiatives such as the Smart Dubai Strategy and DEWA’s Smart Living Programme are accelerating adoption across both high-end and mid-market developments. In Abu Dhabi, the city’s Digital Authority and the Department of Municipalities and Transport (DMT) are advancing a parallel shift through their Smart City Framework and mandates for sustainability in new housing projects — particularly in master-planned communities like Al Reem Island, Saadiyat Grove, and Yas Bay.
For investors, smart homes offer enhanced operational efficiency, stronger rental income potential, and higher resale value. For end-users, they deliver tangible benefits in comfort, sustainability, and digital convenience.
As both cities move toward long-term visions aligned with technology and livability — Dubai through its 2040 Urban Master Plan, and Abu Dhabi through its 2030 Vision — smart real estate is emerging as a resilient, future-proof asset class across the UAE.
2. Introduction
2.1 Dubai
Smart home technology is rapidly becoming a cornerstone of Dubai’s residential property market. What was once a niche offering is now reshaping buyer expectations, pricing strategies, and investor outlooks across the emirate. As Dubai advances toward its Smart City ambitions, smart real estate in Dubai is emerging as a key pillar of long-term urban and economic planning.
Several government-led initiatives are reinforcing this shift, placing technology at the heart of the city's real estate vision:
Dubai Smart City Strategy – Introduced in 2014, this initiative aims to position Dubai as the world’s smartest city. It promotes digital integration across infrastructure, energy, mobility, and urban planning. Within this framework, smart homes in Dubai are a natural progression, aligning with resident expectations for seamless, connected living.
(Source: Smart Dubai Government Office)Dubai 2040 Urban Master Plan – The blueprint for future urban growth highlights smart, sustainable housing as a foundation of mixed-use communities. Areas like Dubai South, Meydan, and Dubai Creek Harbour are set to benefit from this policy direction, especially as smart technology becomes a standard requirement.
(Source: Dubai Municipality, 2021)DEWA’s Smart Living Programme – Operated by the Dubai Electricity and Water Authority, this initiative enables real-time monitoring of water and energy usage. Properties integrated with DEWA’s smart metering and analytics tools are increasingly favoured by both residents and investors seeking green home investments in Dubai.
(Source: DEWA, 2023)Green Building Regulations (GBRS) – Mandatory for all new builds, these standards encourage the use of energy-efficient smart home systems such as automated lighting, HVAC optimisation, and smart control hubs — all of which reduce operating costs and support sustainability mandates.
(Source: Dubai Municipality, 2016)
For developers, embedding smart infrastructure into new communities is not just about compliance — it's a strategy to future-proof assets and enhance market appeal. In parallel, property investors in Dubai are recognising the long-term value of homes that offer operational efficiency, tenant demand, and technology-enabled differentiation.
This report explores the tangible impact of home automation in Dubai on real estate values. Through data insights, case studies, and pricing comparisons, we assess how smart technology is transforming not just the way homes are lived in — but how they are valued, rented, and sold.
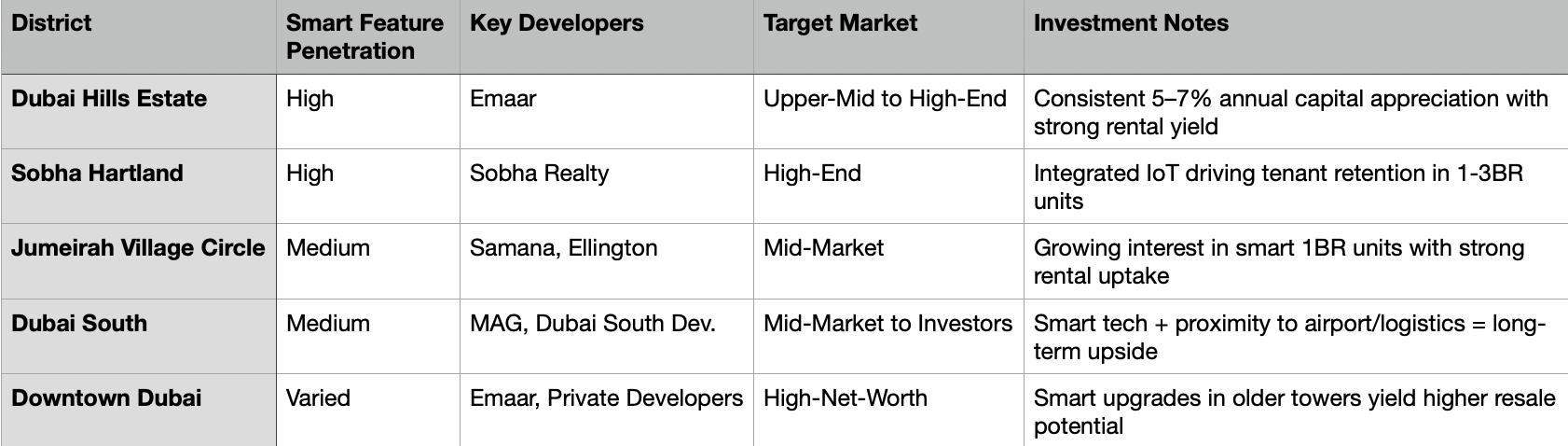
NOTE: Dubai Smart Home District Comparison
2.2 Abu Dhabi
Smart home technology is quietly but steadily becoming a cornerstone of Abu Dhabi’s residential real estate market. While the capital has traditionally taken a more measured approach to digital transformation, the momentum is now unmistakable. As Abu Dhabi aligns with its long-term sustainability and digital infrastructure goals, smart-enabled properties are emerging as a strategic pillar of its urban growth narrative.
Several government-led programmes and regulatory bodies are shaping this transition, embedding technology into the DNA of the city’s real estate sector:
Abu Dhabi Vision 2030 – This overarching development framework prioritises sustainability, livability, and innovation across the capital’s built environment. Within this strategy, smart housing plays a growing role in achieving both environmental and economic resilience. (Source: Urban Planning Council, Abu Dhabi)
Abu Dhabi Smart City Framework – Led by the Abu Dhabi Digital Authority (ADDA), this framework lays the foundation for digital infrastructure across transport, utilities, and urban planning. In the real estate sector, it facilitates the integration of smart energy systems, remote diagnostics, and data-driven community management platforms. (Source: ADDA, 2022)
Estidama Pearl Rating System – Unique to Abu Dhabi, this mandatory sustainability rating promotes green building design. The programme naturally intersects with smart home adoption through incentives for energy-efficient lighting, HVAC optimisation, and intelligent water usage systems. (Source: Department of Municipalities and Transport, 2020)
New Community Mandates from the DMT – The Department of Municipalities and Transport (DMT) has introduced a series of guidelines promoting tech-forward infrastructure in upcoming communities, particularly in zones like Yas Island, Saadiyat Grove, and Al Reem Island. Developers are increasingly incorporating smart metering, app-based automation, and AI-supported building management as a competitive standard. (Source: DMT Circulars, 2023)
For developers, the integration of smart infrastructure is both a compliance requirement and a market opportunity — particularly as Abu Dhabi’s tenant base becomes younger, more international, and digitally inclined. Properties that offer remote control of lighting, energy management, security, and appliance scheduling are not just seen as luxuries, but as expected features in high-performance homes.
From an investor perspective, smart home real estate in Abu Dhabi presents an opportunity to enhance rental stability, operational efficiency, and long-term asset value. The capital’s more controlled development pipeline offers a strategic advantage: smart technology can be embedded from the planning stage, reducing retrofitting costs and boosting lifecycle value.
This report examines the measurable impact of home automation in Abu Dhabi on real estate values, buyer preferences, and investor returns. Through pricing comparisons, district-level insights, and a review of policy frameworks, we assess how smart technology is redefining residential property benchmarks in the UAE’s capital city.
NOTE: Abu Dhabi Smart Home District Comparison
3. Smart Home Technology Adoption in Dubai & Abu Dhabi
Smart home adoption is advancing across the UAE’s two leading real estate hubs — Dubai and Abu Dhabi — each guided by its own regulatory environment, development philosophy, and investor focus. While Dubai pushes forward through private-sector innovation and market competition, Abu Dhabi’s transformation is driven by public policy and planned execution. This section explores how both cities are building their smart home ecosystems and what that means for long-term value creation.
3.1 Dubai’s Smart Home Market: Leading Innovation in Real Estate Technology
Dubai has emerged as the UAE’s fastest-moving smart home market, supported by a combination of government incentives, developer ambition, and digital-savvy consumer demand. Policies such as the Smart Dubai Strategy, Green Building Regulations, and DEWA’s Smart Living Programme have accelerated the shift toward integrated automation in both new and retrofitted residential assets.
In-demand features across Dubai include:
IoT-based energy and climate control systems
Motion-sensing lighting and app-controlled smart hubs
DEWA-linked utility monitoring
Remote security access, facial recognition, and smart intercoms
These features are now a core offering in projects by leading developers like Emaar, Ellington, Sobha, and MAG, especially in high-performance communities such as:
Dubai Hills Estate 🟩
Sobha Hartland 🟩
Downtown Dubai (select towers) 🟩
Jumeirah Village Circle (JVC) 🟨
Arjan & Meydan (select mid-market smart builds) 🟨
In parallel, the IoT property sector in Dubai is being reinforced by proptech startups and smart system integrators, contributing to a broader transformation in how properties are managed, lived in, and priced.
3.2 Abu Dhabi’s Smart Real Estate Strategy: Policy-Led and Premium Focused
Abu Dhabi’s approach to smart home adoption is more strategic and centrally guided. Under the direction of Abu Dhabi Vision 2030, the Smart City Framework, and the Estidama Pearl Rating System, new developments are being designed from the ground up with embedded technology for sustainability, efficiency, and data-driven living.
Smart home technology in Abu Dhabi is most visible in:
Saadiyat Grove 🟩 – A cultural and residential flagship by Aldar, fully equipped with automation, energy controls, and community-wide smart integration.
Al Reem Island 🟨 – A mix of legacy towers and new smart-enabled projects, popular with mid-to-high-end renters and long-stay expats.
Yas Island 🟨 – A rising hotspot for short-term rentals, often bundled with app-based automation and digital concierge services.
Al Maryah Island 🟩 – Executive housing with premium smart infrastructure, near the capital’s financial district.
Al Raha Beach 🟥 – A mature district with limited smart penetration but strong long-term rental appeal.
Unlike Dubai, where some smart systems are added post-handover, Abu Dhabi’s newer developments are embedding automation during the planning and infrastructure stages — lowering retrofit costs and aligning with DMT compliance requirements.
3.3 Comparative Insights: Dubai vs Abu Dhabi Smart Property Trends
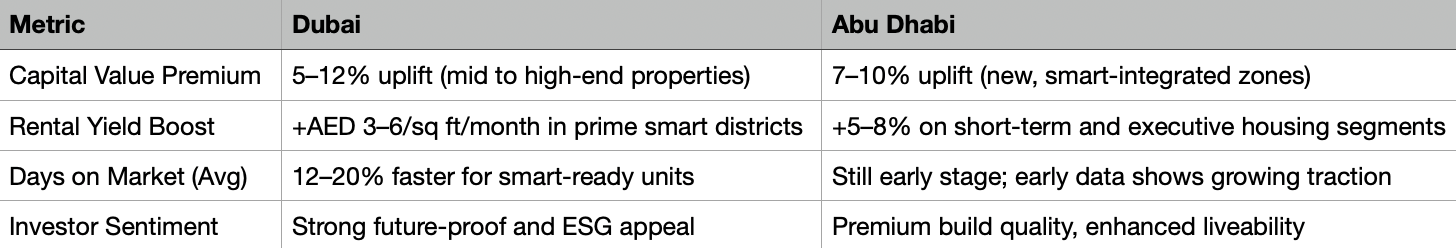
NOTE: Dubai vs Abu Dhabi Smart Property Trends
4. Impact of Smart Home Technology on Property Values in Dubai & Abu Dhabi
Smart home technology is now a defining value metric in UAE real estate — particularly in fast-evolving residential zones across Dubai and Abu Dhabi. As buyer preferences shift towards connected, energy-efficient living, properties equipped with integrated automation are commanding measurable premiums in both capital value and rental performance. This section explores how home automation in the UAE is influencing real estate valuations, resale dynamics, and marketability.
4.1 Capital Value Premiums: Future-Ready Homes, Higher Price Tags
In Dubai, smart-enabled properties in areas like Dubai Hills Estate, Sobha Hartland, and select towers in Downtown Dubai have recorded price premiums of 5–12% over traditional stock. Key drivers include:
Perceived future-proofing and operational cost savings
Demand from tech-savvy investors and younger expat buyers
Market preference for sustainable, digitally managed homes
In Abu Dhabi, where smart home integration is most prominent in new master-planned zones, capital appreciation for smart properties is averaging 7–10%. Developments such as Saadiyat Grove, Yas Island, and Al Maryah Island are leading the charge, setting new benchmarks for tech-enabled urban living.
4.2 Rental Yield Advantages: Appealing to the Connected Tenant
Smart homes are increasingly commanding rental premiums due to their appeal to a digital-native tenant base. In Dubai, smart-ready properties benefit from:
Higher occupancy rates, especially in 1–2 bedroom units
Rental premiums of AED 3–6 per sq ft/month, particularly in JVC, Meydan, and Downtown
Greater demand for short-term rentals equipped with remote automation
In Abu Dhabi, smart-enabled properties in executive communities (e.g. Al Reem Island, Yas Bay) are seeing rental uplifts of 5–8%, particularly among foreign professionals and long-stay business travellers.
4.3 Resale Value & Marketability: Faster Turnover, Stronger Appeal
Across both emirates, smart homes are selling faster than their traditional counterparts — with shorter days on market and stronger lead conversion from online listings.
In Dubai, developers like Emaar and Ellington have capitalised on this trend by standardising automation in off-plan marketing.
In Abu Dhabi, Aldar’s projects on Saadiyat and Yas Islands are seeing growing resale interest from high-net-worth buyers looking for lifestyle automation, not just square footage.
Smart features are increasingly seen as a marker of build quality, aligning with rising demand for energy-efficient homes in the UAE and digitally managed living environments.
4.4 Long-Term Impact on the Property Market
The widespread integration of smart features is creating two notable trends:
Elevated Resale Expectations: Buyers and investors anticipate smart systems as standard in mid-to-high-end housing.
Pressure on Legacy Stock: Older properties without automation are becoming less competitive, particularly in urban zones where new developments set the digital benchmark.
NOTE: Value Uplift from Smart Home Integration
5. Smart Home ROI for Investors
Smart homes are no longer just a lifestyle trend — they are now shaping return expectations for real estate investors in Dubai and Abu Dhabi. As automation becomes more standardised, investors are leveraging it to enhance rental yields, reduce overheads, and strengthen long-term value. This section breaks down how investing in smart homes in the UAEtranslates into real financial performance.
5.1 Upfront Costs vs Long-Term Gains
The initial investment in smart technology — typically AED 10,000–25,000 per unit for lighting, climate control, and security — is proving to deliver strong ROI, especially in new builds.
In Dubai, developers like Ellington and Samana have integrated smart systems into mid-market offerings, enabling landlords to attract premium tenants with little additional CapEx. In high-end areas like Sobha Hartland and Dubai Hills Estate, buyers now expect full smart integration as a standard feature — positioning these assets as more resilient in future resale cycles.
In Abu Dhabi, the cost advantage is even stronger. Projects in Saadiyat Grove, Yas Island, and Al Maryah Islandembed automation during development, lowering integration costs and boosting long-term value. These homes also align with Estidama sustainability standards, increasing regulatory compliance and investment appeal.
5.2 Rental Income Performance: Quantifying the Uplift
Smart homes are increasingly outperforming traditional units in rental returns:
In Dubai’s JVC and Meydan, 1–2 bedroom smart apartments are achieving 6.5%–7.5% gross yields, compared to 5.5%–6.2% for non-smart equivalents.
In Abu Dhabi, executive short-let units on Yas Island or Al Reem Island are exceeding 8% annual returns, driven by automation features and tech-forward tenant preferences.
Key drivers include:
Higher tenant satisfaction and retention
Premium pricing potential
Attractiveness to the short-term rental market where remote control and smart access are valued
5.3 Operational Efficiency for Landlords
Smart properties also reduce long-term overheads:
Lower utility bills via smart HVAC, thermostats, and lighting
Preventative maintenance with real-time system diagnostics
Remote management tools that simplify oversight for overseas investors
For landlords managing multiple units, the cumulative savings and automation significantly improve net returns and reduce vacancy risks.
5.4 Investment Differentiation & ESG Alignment
Smart homes are now a recognised niche in real estate investment portfolios. Their appeal is growing among:
ESG-focused investors targeting sustainable and efficient buildings
Institutional landlords seeking stable, tech-integrated assets
Cross-border buyers from Europe, China, and the GCC, where digital living is fast becoming the norm
In both cities, digitally enabled real estate is not just a trend — it’s a future-proof strategy. Early adopters are likely to benefit from long-term capital preservation, strong tenant loyalty, and portfolio-level resilience.
NOTE: ROI Snapshot
6. Risks & Challenges of Investing in Smart Homes in the UAE
While smart home technology is transforming the property market in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, it also introduces a new set of investor risks. From system obsolescence to cybersecurity, and retrofitting difficulties to regulatory inconsistencies, understanding these risks is essential for buyers and developers looking to maximise returns while avoiding avoidable pitfalls.
6.1 Rapid Tech Obsolescence: Staying Ahead of the Curve
Smart home systems evolve quickly — what’s cutting-edge today may be outdated within 3–5 years. This creates a potential depreciation risk for properties that rely on outdated platforms or closed proprietary systems.
Risks Include:
Expensive future upgrades
Compatibility issues with evolving tech standards
Buyer resistance to outdated interfaces
Investor Tip: Focus on developments using open-standard systems like KNX, Zigbee, or Z-Wave to ensure future adaptability.
6.2 Cybersecurity & Data Privacy Risks
As homes become smarter, they also become more exposed. From connected locks to voice assistants, every new smart feature introduces potential entry points for cyber breaches — especially in systems lacking robust encryption.
Potential Issues:
Data leaks or hacking of resident information
Legal liability under the UAE’s Federal Data Protection Law (No. 45 of 2021)
Reduced tenant trust in poorly secured units
Dubai vs Abu Dhabi Insight: Tier 1 developers often partner with tech giants like Schneider or Honeywell. Risk is more prevalent in smaller-scale projects using generic off-the-shelf systems.
6.3 Retrofitting Older Properties: High Cost, Low Impact
Many mid- and lower-tier communities across Al Barsha South, Deira, and parts of Khalidiya in Abu Dhabi present limited viability for smart home retrofitting.
Barriers:
Electrical rewiring requirements
High install costs vs potential ROI
Limited tenant willingness to pay higher rents for minor upgrades
Recommendation: Retrofitting only makes sense in units with high turnover, in strategic emerging locations, or for long-term yield optimisation.
6.4 Overhyped Features with Low Value Add
Some projects aggressively market gimmicky smart features (e.g. coloured LED mood lighting or smart mirrors) with little impact on property value or rental yield.
Downside Risks:
Buyer scepticism post-handover
Reduced resale appeal
Overpricing vs functional performance
Investor Focus: Prioritise core automation systems — energy management, climate control, and access — over novelty.
6.5 Inconsistent Standards & Utility Integration Gaps
Despite progress from DEWA and ADDC, integration of smart systems with utility providers still varies by project and district.
Key Gaps:
Lack of standardised smart certification for residential buildings
Smart meter rollouts inconsistent across mid-market stock
No unified performance rating for “smart readiness”
What’s Needed: A UAE-wide smart property rating system could help define minimum standards, similar to Estidama or LEED, giving investors more clarity and confidence.
7. Future Outlook (2025–2030): What’s Next for Smart Homes in the UAE
Smart homes are on track to become the new standard in Dubai and Abu Dhabi’s residential property landscape. As policy, infrastructure, and consumer behaviour evolve in tandem, the next five years will bring a wave of transformation — moving smart real estate from luxury feature to foundational expectation.
7.1 Full Integration in New Residential Developments
By 2030, smart home integration in Dubai and Abu Dhabi is expected to be standard in most mid- to high-end developments — driven by:
Stricter green building mandates
Developer competition in the off-plan segment
Buyer demand for energy-efficient and tech-ready homes
Where it’s happening:
In Dubai: Expect widespread integration in Dubai Creek Harbour, Meydan, and upcoming phases of Dubai South
In Abu Dhabi: Projects aligned with Estidama and DMT smart city initiatives will lead — particularly in Yas Island, Masdar, and Al Reem
7.2 Creation of Smart Home Certification Standards
To support investor confidence and transparency, we anticipate the rollout of UAE-specific benchmarks such as:
Smart Readiness Index (SRI-UAE) — measuring automation, interoperability, and energy optimisation
Inclusion of smart features within RERA valuation reports and property listing filters
Cross-integration with Estidama, LEED, or a new DMT "Smart Certified" label
Impact for investors: A formal rating system will make it easier to compare and value smart properties — improving price discovery, resale planning, and portfolio screening.
7.3 Growing Role of Institutional Investment in Smart Housing
As yields stabilise in core real estate sectors, institutional capital is moving toward smart, tech-enabled assets. Between 2025–2030, we expect:
Launch of smart REITs focusing on ESG-aligned assets
Greater BTR (Build-to-Rent) schemes using smart automation for cost-efficiency
Strategic alliances between proptech platforms and master developers
Smart-enabled portfolios will appeal to cross-border investors, family offices, and sovereign wealth funds focused on resilient, tech-forward housing.
7.4 Expansion of Digitally Managed Smart Districts
The next wave of master-planned districts will prioritise smart infrastructure as standard — not add-on.
Dubai Targets:
Dubai South Phase 2
Meydan Horizon + Arjan East verticals
Smart pocket communities in JVC and Al Furjan
Abu Dhabi Focus:
Masdar City’s smart residential cluster
Yas South expansion zones
Digitally controlled infrastructure in Al Reem’s core grid
These zones will offer end-to-end connected living — where energy, mobility, and housing converge through a smart city framework.
7.5 Integration with AI, Blockchain, and Renewable Energy Ecosystems
Looking beyond 2026, the smart home will evolve into a digitally intelligent asset — interacting with broader urban platforms.
What’s Coming:
AI-managed home systems that adjust to usage patterns and weather
Blockchain smart contracts for maintenance, leasing, and security
Integration with DEWA/ADDC smart grid platforms, enabling real-time carbon tracking and bill settlement
This will redefine the value proposition of UAE smart homes — turning them into secure, responsive, and energy-aware components of next-gen real estate.
8. Smart Home Investment & Buying Recommendations in Dubai and Abu Dhabi
As smart homes become increasingly mainstream in the UAE, both investors and homebuyers need to make informed, future-ready decisions. With features ranging from energy automation to voice control and app-based security, smart homes in Dubai and Abu Dhabi are evolving beyond trend — they’re becoming investment-grade assets and lifestyle essentials.
Here’s what investors and end-users should know before stepping into the UAE’s smart home market.
8.1 Investor Guide: Building a Smart-Ready Property Portfolio
1. Invest in Core Automation — Not Flashy Gimmicks
Look for properties that include smart essentials like:
Climate control
Lighting automation
Smart locks and video security
Energy dashboards linked to DEWA or ADDC
Avoid overpaying for flashy extras (e.g. smart mirrors, voice-activated curtains) with limited ROI.
2. Prioritise Open-Source Systems
Properties using KNX, Zigbee, or Z-Wave allow for easier upgrades and broader device compatibility — a long-term advantage over closed platforms.
3. Target Smart Growth Districts
High potential zones include:
Dubai: Arjan, Meydan, Dubai Creek Harbour
Abu Dhabi: Reem Island, Masdar City, Yas South
These areas align with government tech strategies and offer better capital appreciation and tenant demand.
4. Align with ESG & Efficiency Goals
Smart homes that support energy efficiency, water management, and green certifications like Estidama or LEED will attract future-conscious buyers and tenants.
5. Focus on BTR & Short-Term Smart Investments
Automated units are ideal for:
Remote management
Dynamic pricing
Guest access automation
This makes them perfect for build-to-rent portfolios and holiday let markets.
8.2 Buyer Guide: Choosing a Future-Proof Smart Home
1. Evaluate Smart Infrastructure
Look for:
Integrated energy management
App-controlled lighting and devices
Smart access and security features
Compatibility with Alexa, Google Home, or Apple HomeKit
2. Confirm Real Energy Savings
Request recent DEWA or ADDC utility bills to validate energy efficiency claims. Some smart homes can reduce utility usage by up to 25–30%.
3. Check Privacy & Security Standards
Ask whether the system:
Encrypts your data
Allows for full user control
Stores info on local or secure cloud servers
Tip: Reputable developers often use GDPR-compliant systems. Always check if smaller developers meet UAE Data Law requirements.
4. Confirm Upgrade & Service Flexibility
Ensure your system supports:
Over-the-air updates
Modular expansion
Local service support or global tech partnerships
5. Look Beyond the Tech — Prioritise Value
Focus on how smart features support:
Everyday convenience
Reduced running costs
Long-term resale appeal
A smart home should empower how you live — not just how it looks on paper.
Executive Summary
Smart Home Technology is Redefining Real Estate in Dubai and Abu Dhabi
In the UAE’s rapidly evolving property market, smart home technology is no longer optional — it’s a critical driver of property value, buyer preference, and investment performance. This report explores how automation, connectivity, and energy efficiency are transforming real estate in Dubai and Abu Dhabi, with clear implications for investors, developers, and end-users.
Key Market Insights
6–10% Price Premium: Smart-enabled homes in key UAE districts (e.g. Dubai South, Arjan, Masdar City, Reem Island) consistently outperform non-smart units in resale value.
Higher Rental Yields: Smart properties in Dubai and Abu Dhabi deliver 1.2%–1.8% stronger gross yields, driven by rising tenant demand for intelligent living spaces.
70% of Buyers Prefer Smart Homes: Surveys show a decisive shift in buyer expectations, with tech-enabled features becoming a standard selection criterion.
Policy Support is Strong: Initiatives like the Dubai Smart City Strategy, DEWA’s Smart Living Programme, and Abu Dhabi’s Estidama framework are embedding smart systems into real estate development norms.
What This Means for Investors
Target smart-enabled developments for higher long-term appreciation.
Focus on open tech platforms and ESG-aligned properties to future-proof your portfolio.
Explore growth corridors with integrated smart infrastructure — especially off-plan assets in emerging districts.
Smart Homes for End-Users
Prioritise core automation (climate, lighting, access) over flashy tech.
Demand transparency on energy savings and smart service fees.
Choose properties built on scalable, upgradable systems — not closed ecosystems.
The Road Ahead
By 2030, smart home technology in the UAE will shift from value-added to value-expected. Regulatory evolution, proptech-driven investment platforms, and tenant sophistication will make smart-ready assets the new standard.
Bottom line:
Whether you’re an investor, homebuyer, or real estate professional, understanding the value of smart homes today will define your position in the UAE property market tomorrow.